
Introducing advanced automation
Automation is the future of technology, so it was only a matter of time until it was introduced to the HVLS fan category. New systems featuring integrative technology for automatic fan control eliminate the need to constantly monitor and adjust fan speed and direction in response to temperature fluctuations. These assemblies identify and dictate optimal operating speed and direction for each fan based on the facility’s temperature and humidity, allowing the user to set up controls to manage when the fans run.
Advanced climate control systems are available that measure temperature and humidity at two points, calculates the heat index, and identifies the best operating speed and direction for each fan. The user selects a desired temperature range, and as the indoor temperature rises above the specified range, the fans automatically run in the forward direction at the best speed to create an appropriate cooling effect. When the indoor temperature drops below the selected temperature range, the fans automatically reverse to redistribute the heated air overhead, effectively eliminating hot and cold spots without generating a discernable breeze.
The following is an example of control features available to optimize HVLS fans. Through just one controller, users can manage up to 30 fans, with the versatility to divide these fans into four zones. With zoning, the user can customize fan operation parameters for specific areas like welding or the office. There are two sensors per zone—one at the ceiling and the other at the floor—gathering humidity and temperature data. They are independent, external sensors, so the controller can be mounted in a different room than the fans and sensors. The software then takes the temperature and humidity measurements from the sensors and calculates the heat index to understand what the temperature feels like due to humidity, rather than just the air temperature.
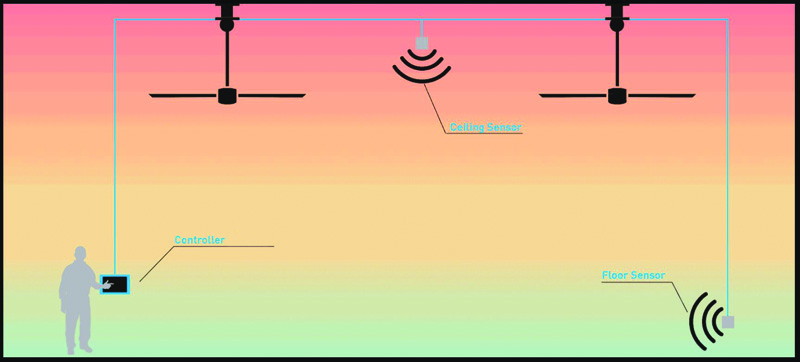
For such control systems, each fan model and diameter with its corresponding airflow production is programmed into the software. The system uses an advanced algorithm to determine the speed and direction based on the type of fan, the blade size, and the distance between the closest wall or fan, delivering the desired effective temperature.
When the fans are coupled with air-conditioning, the cooling effect delivered by the fans reduces the load on the air-conditioner, decreasing utility spend. In the winter, mixing the heated air will eliminate hot and cold spots, leading to savings on heating costs. Automation enables the fans to be fully optimized, maximizes energy efficiency, and provides continuous occupant comfort.
Conclusion
Since the invention of the HVLS fan in 1998, fan companies remain committed to the continual innovation and design of large, cost-effective commercial ceiling fans. Today, a wide range of HVLS fans are offered for various industries and applications, including:
- barn, agricultural, and horse and livestock fans;
- commercial ceiling fans;
- industrial warehouse and manufacturing fans;
- military fans;
- aviation fans;
- auto service fans;
- retail space fans; and
- fitness center cooling fans.
Architects and engineers are specifying new installations combining the incredible efficiency with the industrial design features of HVLS fans. It may have started in a dairy barn in Southern California, but the multi-million-dollar HVLS revolution has spread to every corner of the globe.




