Specifying the right privacy and shading
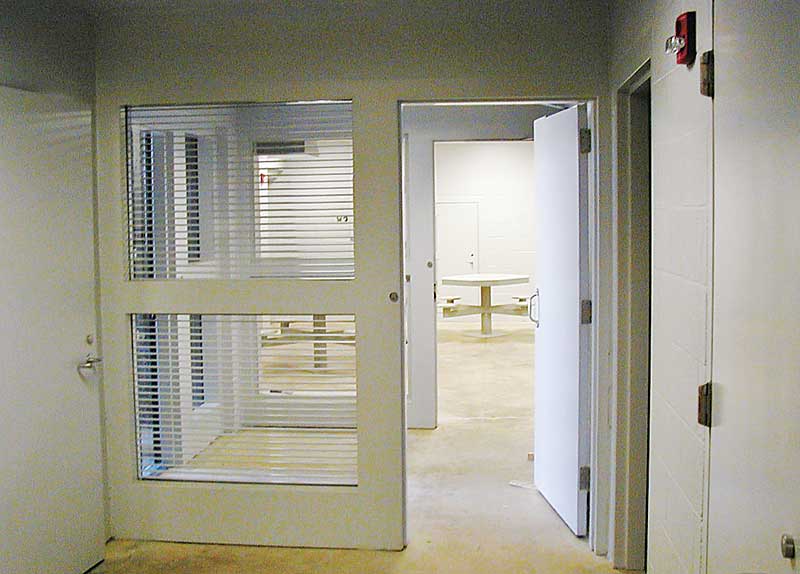

Art galleries and museums
Museums and art galleries, along with other buildings designed to showcase house and protect items of value, require discerning architectural design. Daylight enhances and adds beauty to exhibits and interiors, but it can also usher in damaging ultraviolet (UV) rays, unwanted heat, and glare. Using ample glazing is an essential part of creating beautiful art-oriented and cultural spaces, but this also necessitates effective sunlight management.
Integrated louvers once again provide an advantage over blinds, as they help ensure optimal daylight management. They provide the maximum levels of daylight, heat, and light control that galleries and museums need to protect exhibits from damaging UV rays. Louvers also permit the flexibility of design required to suit even the most unique architectural requirements. To filter light in the most efficient manner, they can be specified into sloped, vertical, flat, and overhead glazing. Their alignment is not affected by glass inclination—whether in vertical or sloped glazing. However, if integrated blinds are not installed perfectly vertical, they will sag and not stay aligned.
Detailed specification considerations
Once integrated solution has been chosen for the building design, the next step is to specify the detailed product requirements.
Regulatory requirements
Based on the application, integrated solutions need to comply with certain safety and quality assurance standards, including:
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Z97.1, Safety Performance Specifications and Methods of Test for Safety Glazing Material Used in Buildings;
- ASTM C50, Standard Specification for Elastomeric Cellular Preformed Gasket and Sealing Material;
- ASTM C920, Standard Specification for Elastomeric Joint Sealants;
- ASTM C1036, Standard Specification for Flat Glass;
- ASTM C1048, Standard Specification for Heat-treated Flat Glass-Kind HS, Kind FT, Coated and Uncoated Glass;
- ASTM C1115, Standard Specification for Dense Elastomeric Silicone Rubber Gaskets and Accessories;
- ASTM E2190, Standard Specification for Insulating Glass Unit Performance and Evaluation;
- Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) 16 CFR 1201, Safety Standard for Architectural Glazing Materials;
- Glass Association of North America (GANA) Engineering Standards Manual and Glazing Manual;
- National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 80, Standard for Fire Doors and Other Opening Protectives;
- Underwriters Laboratories (UL) 9, Standard for Fire Tests of Window Assemblies;
- UL 10B, Standard for Fire Tests of Door Assemblies;
- UL 10C, Standard for Positive Pressure Fire Tests of Door Assemblies; and
- Insulating Glass Manufacturers Association (IGMA) TB-3001, Sloped Glazing Guidelines.

Warranties
Warranties for integrated solutions need to consider both interior and exterior applications. These should include specific coverage against material-obstruction of vision as a result of dust or film formation on the internal glass surface caused by failure of the hermetic seal other than through glass breakage. Additionally, warranties should cover any internal parts for malfunction, mechanism failure, or premature wear.
Glazing
Both integrated louvers and blinds can vary depending on the building type, orientation, application, and daylighting requirements, including:
- fire-rated glass specifications need to consider composition, UL listing, fire rating, and thickness;
- clear and tinted tempered glass specifications need to include ASTM and ANSI standards, type and class of glass (tinted heat-absorbing and light-reducing), quality of glazing, and tempered values;
- plastic glazing specifications (e.g. for X-ray rooms) need to consider the type of polycarbonate required (polycarbonates should only be used in interior locations), type (e.g. plastic compound, UV-stabilized, non-yellowing, abrasion, resistant-coated), and color (e.g. clear, translucent, grey tint, bronze tint etc.);
- lead glass specifications need to consider the lead equivalency required—lead glass is not available tempered, therefore in high-impact areas (e.g. doors and sidelites), laminated lead glass will satisfy safety-glazing requirements; and
- glass-clad polycarbonate glazing specifications may need to consider the level of attack-resistance required in applications like correctional facilities or mental health institutions—glazing thicknesses start at 177 mm (7⁄16 in.) thick and increase according to level of attack. Other safety/protection standards may also need to be considered for such glazing.
For integrated louvers in exterior applications, additional glazing considerations include glass deflection, application type such as sloped or vertical, design loads, and climate according to the project location. Specifications for argon gas for improved thermal performance may also be considered.