
Surface preparation
The degree of surface preparation will depend on the thickness of the flooring system. A thinner system requires less preparation than a thick, mortar one. In all cases, specifications should include clear language addressing the removal of “laitance, curing compounds, hardeners, sealers, and other contaminants,” and should reference NACE No. 6/Society for Protective Coatings (SSPC)-SP 13-2018, Surface Preparation of Concrete, which outlines minimum acceptance criteria of the concrete substrate and relevant test methods.
The floor coating industry relies on the International Concrete Repair Institute (ICRI) visual reference standards for degrees of surface preparation from lightest (CSP 1) to heaviest (CSP 10). Thin-film systems generally require an ICRI-CSP 1 to 3, which can be achieved through light shot blast or diamond grinding. (Acid etching is discouraged as it is difficult to assure sufficient profile and full neutralization of acid). Broadcast/laminate and mortar systems accommodate a more aggressive anchor profile, usually listed as minimum of ICRI-CSP 3 or greater and achieved by shot blast, diamond grinding, or scabbling.
Relevant tests for floor coatings
Determining what products to select can be challenging, especially since many floor coatings products look similar on published literature and documents. Specifiers should consider the following performance tests prior to product selection:
- abrasion, per ASTM D4060, Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Organic Coatings by Taber Abraser;
- compressive strength, per ASTM C579, Standard Test Methods for Compressive Strength of Chemical-resistant Mortars, Grouts, Monolithic Surfacings, and Polymer Concretes;
- impact, per ASTM D2794, Standard Test Method for Resistance of Organic Coatings to the Effects of Rapid Deformation; or MIL-D-3134, Military Specification for Deck Covering Materials;
- slip resistance, per ASTM D2047, Standard Test Method
for Static Coefficient of Friction of Polish-coated Flooring Surfaces as Measured by the James Machine; and - cleaning agent resistance, per ASTM D1308, Standard Test Method for Effect of Household Chemicals on Clear and Pigmented Coating Systems.
There are many more tests that may be relevant depending on the actual exposure conditions expected on the project. These could include specific physical attributes such as chemical resistance, UV resistance, and ability to withstand severe free-thaw cycles. A careful review of the project with the coating supplier will identify these parameters to ensure the right product is selected for long-term durability and performance.
Floor to wall transitions
A major benefit of fluid-applied floor coatings over other materials is the ability to tie directly, and seamlessly, into the wall coating system by the creation of a cove base. This continuous transition is durable, hygienic, and creates a “bathtub” effect suitable for wet conditions or frequent cleaning. Often, the same floor coating materials used for a broadcast/laminate or mortar system can be used to build the cove base, or the coating manufacturer may offer a specialized material designed with enough viscosity, or bulk, to properly build the base.
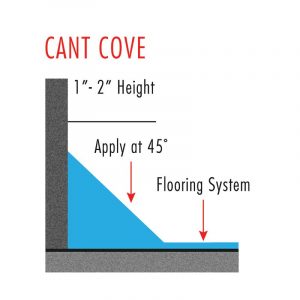
The two most common cove bases are rolled-radius and cant cove (Figure 1). A rolled-radius cove is usually 100 mm (4 in.) high and resembles the plastic, rubber, or wood bases commonly used to trim a room, whereas a cant cove is installed at a 45-degree angle from floor to wall for easier cleaning by eliminating hard right angles. To tie seamlessly into the wall, the cove is either installed before the wall coating, in which case the wall coating is carried down to the cove/wall junction or after the wall system is applied.
Conclusion
The ability to tailor a floor coating system—whether for physical wear, mechanical abuse, or chemical contact—makes high-performance coatings a viable choice for a variety of facility floors. By keying in on the expected physical exposure conditions and aesthetic requirements, thickness and coating types can be determined and specified as a complete system based on their relevant performance data.





