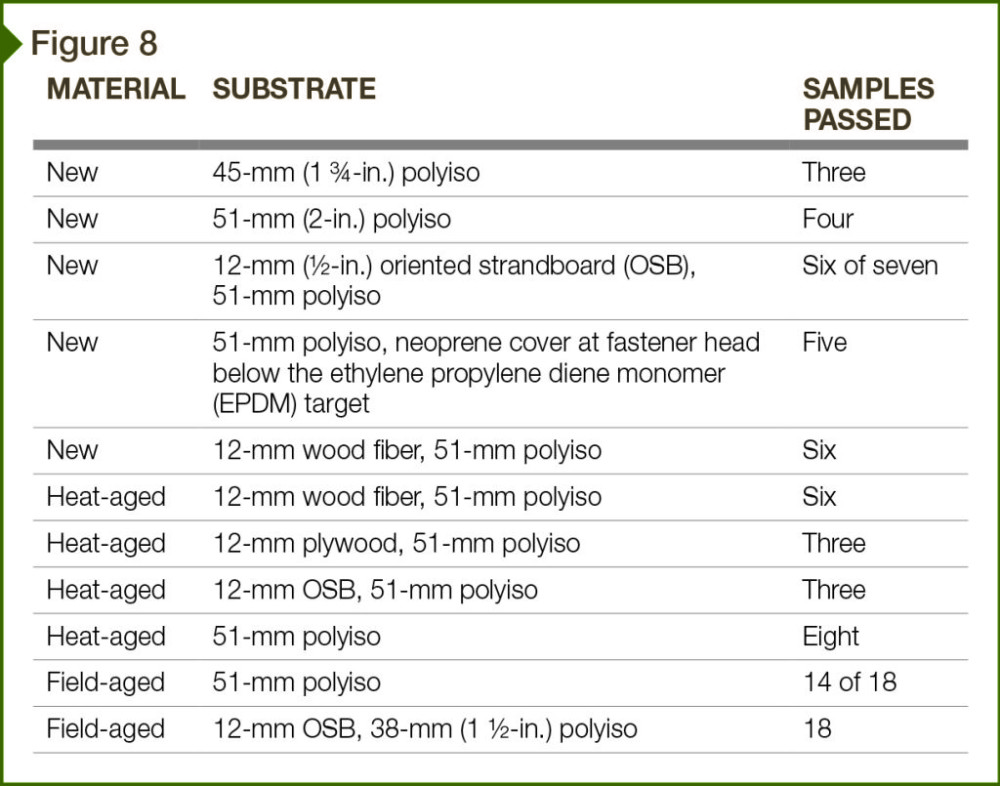
The various targets were impacted both in the ‘field’ area and also directly over fasteners and plates used to secure the substrate below the EPDM. Failure was defined as a visible split or cut in the surface.
Of the 25 ‘new’ EPDM test targets tested, 24 were not damaged by 76-mm hail balls. None of the 20 ‘heat-aged’ targets failed when impacted by this size of hail, however. The ‘field-aged’ EPDM target samples included:
- 18 over a 51-mm (2-in.) thick polyiso insulation substrate; and
- 18 over a 12-mm (1⁄2-in.) thick OSB substrate, supported by 38-mm thick polyiso roof insulation.
Fourteen of the EPDM targets that were adhered directly over the polyiso did not fail when impacted with 76-mm hail balls. (The mode of failure typically is a split or cut in the roof membrane.) One sample failed with a 76-mm hail ball, a second sample failed with a 64-mm one, and the two other samples failed with a 51-mm diameter hail ball. None of the 18 EPDM ‘field-aged’ targets over the OSB were damaged by the 76-mm diameter specimens (Figure 8).
Commentary
Some geographical areas of the United States are clearly more prone to severe hail. Roof assemblies should be capable of resisting impact from reasonably expected hail storms for a given location. Just as roofs are required to perform in various meteorological events, such as wind, snow, and rain—a roof should be able to withstand some degree of hail impact over its expected service life.
In the 2006 International Building Code (IBC), Paragraph 1504.7 of Chapter 15 (“Roof Assemblies and Rooftop Structures”) states roof coverings shall resist impact damage based on tests conducted in accordance with:
- ASTM D3746;
- ASTM D4272, Standard Test Method for Total Energy Impact of Plastic Films By Dart Drop; and
- Canadian General Standards Board (CGSB) 37-GP-52M, Roofing and Waterproofing Membrane, Sheet-applied, Elastomeric.
These procedures are conducted with steel darts versus ice spheres at room temperature. The testing is for new products and does not address the long-term effects of UV exposure. The results of testing following these protocols may provide false positive results.

Jim D. Koontz & Associates—the firm of one of this article’s authors—has examined hundreds of EPDM roofs that have been impacted by hail. Two noteworthy investigations include a telephone building in Fort Worth, Texas, that was impacted by softball-size hail in 1995. The non-reinforced EPDM over polyiso did not fail. A second investigation was at the University of Nebraska in Kearney. All of the campus buildings covered with non-reinforced EPDM survived softball-sized (i.e. 96.5-mm [3.8-in.]) hail. The manufacturer of the roof was notified of the performance of the aged EPDM assembly. The gravel built-up roofing (BUR), metal, slate, clay tile, and modified-bitumen (mod-bit) roof covers on the 65 other university buildings all failed.
During the examination of hundreds of roofs, direct impacts over fasteners and plates used to secure underlayment have been extremely rare. Damage observed of this kind has not constituted a failure of the entire roof, and has been repairable. The increasing use of adhesives to fasten insulation and coverboards is eliminating the already unlikely chance of damage caused by hail impact with mechanical fastener plates.
Conclusion
The new, heat-aged, and aged non-reinforced EPDM tested within this study provided excellent resistance to large hail. Of the 81 targets installed over polyiso, wood fiber, plywood, and OSB, 76 did not fail when impacted with hail balls that were up to 76 mm (3 in.) in diameter.
The overall results clearly indicate non-reinforced EPDM roof assemblies offer a high degree of hail resistance over various substrates, and validate empirical experiences. The impact resistance of both the field-aged and heat-aged membrane also demonstrates EPDM retains the bulk of its impact resistance as it ages.
Owners of critical facilities—hospitals, schools, data centers, airports, and sensitive government buildings—demand durability and long-term service lives of their roofs. The use of non-reinforced EPDM can provide an additional level of long-term protection, especially in hail-prone areas.




