:
Thin bricks are manufactured to the requirements provided in ASTM C1088, Standard Specification for Thin Veneer Brick Units Made from Clay or Shale. The grade defined in ASTM C1088 for use as an exterior cladding is straightforward, exterior. Similar to the more common ASTM C216, Standard Specification for Facing Brick (Solid Masonry Units Made from Clay or Shale), there are three types of thin brick units:
- TBA (no specified dimensional tolerances);
- TBS (for general use); and
- TBX (where dimensional tolerances are important).
While there is not a minimum prescribed thickness for thin bricks, code requirement limits the maximum thickness of thin bricks. The Masonry Society (TMS) 402, Building Code Requirements for Masonry Structures, which is referenced in the IBC, limits the maximum thickness of adhered units to 67 mm (2 5/8 in.) and less than 73 kg/m2 (15 psf).
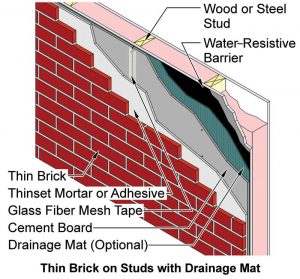
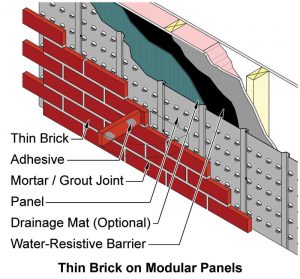
Adhered brick veneer can be employed where providing support for heavier, anchored brick veneer may be difficult. Thin brick veneer may be installed by masons, tile setters, or other workers. Some manufacturers can match thin brick with brick used in anchored veneer applications found elsewhere on the building.
System descriptions
Applied either on- or off-site, thin brick veneer is bonded to, and dependent upon, backing for stability and strength. Bond is achieved by embedding the thin bricks in a mortar or polymer-modified mortar setting bed, or by applying a non-sagging adhesive to the back of the brick and pressing the thin bricks on a panel substrate material. The adhesive must be compatible with the thin brick unit and the substrate, and applied according to the the adhesive or panel manufacturer’s instructions.




